Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots to automate repetitive, manual and high-volume tasks usually carried out by humans. By simulating human interaction with applications and systems, RPA helps to optimize workflows, increase efficiency and reduce errors, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Benefits of RPA
- Reducing Costs and Increasing Productivity: The automation of routine tasks eliminates the need for manual intervention in time-consuming processes, allowing companies to reduce their operating costs. In addition, RPA can operate 24/7, increasing productivity and enabling greater responsiveness to market demands.
- Accuracy and Compliance: Software robots perform tasks exactly as they have been programmed, reducing the likelihood of human error and ensuring that processes meet compliance requirements. This is especially important in regulated sectors such as finance and healthcare, where mistakes can be costly and lead to legal consequences.
- Scalability and Flexibility: RPA can be scaled to meet fluctuations in workload, offering the flexibility to adapt processes according to business needs. In addition, robots can be developed for specific processes or integrated into a broader automation strategy.
- Customer and employee experience: By eliminating repetitive tasks, employees have more time to focus on activities that require creativity and human interaction, improving the experience at work. This, in turn, can lead to faster and more personalized customer service.
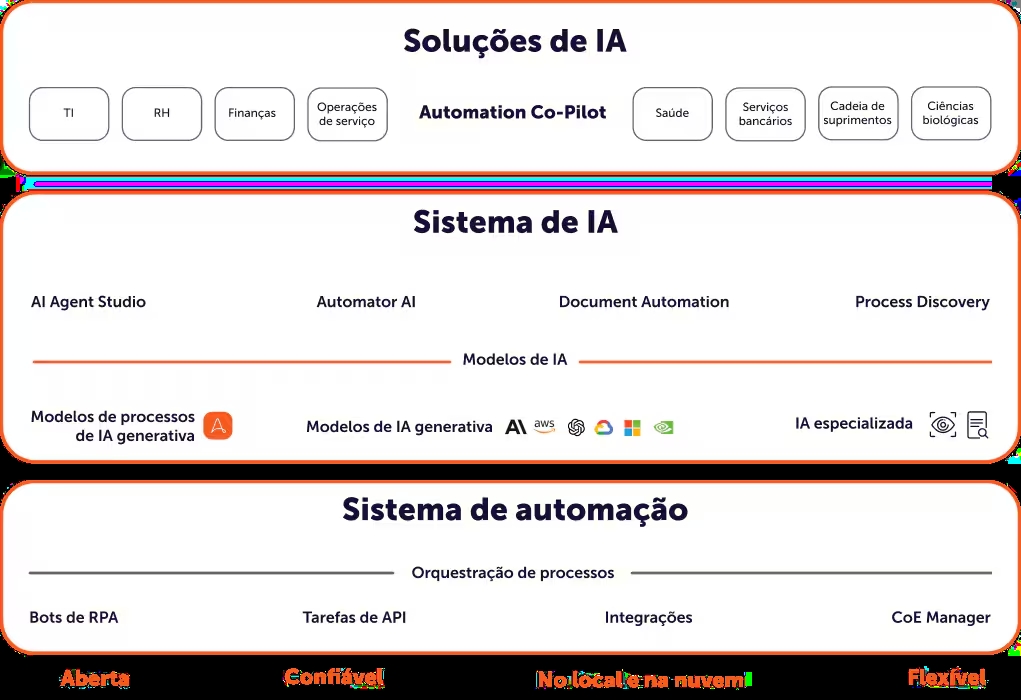
Key Concepts
Center of Excellence (CoE)
The Center of Excellence (CoE) is an organizational model that aims to centralize and standardize RPA initiatives within a company. An RPA CoE is responsible for defining the automation strategy, developing best practices, providing technical support and monitoring the performance of the robots in operation.
By establishing a CoE, the company creates a governance environment for automation, promoting consistency and control over RPA projects. This also facilitates the sharing of knowledge and increases the organization's maturity in the use of RPA, allowing for a scalable and effective implementation.
Process Discovery
Process discovery is a crucial stage in RPA, as it identifies the workflows that would most benefit from automation. To do this, tools are used to observe and analyze current processes, identifying bottlenecks and repetitive steps, as well as identifying opportunities for automation.
This discovery allows the organization to prioritize the most suitable processes for automation, optimizing resources and maximizing the return on investment (ROI) in RPA. From the discovery of processes, the company can put together an automation portfolio, creating an implementation roadmap based on the feasibility and impact of automation on each process.
Document Automation
Document automation is a powerful extension of RPA, especially in sectors that deal with large volumes of unstructured data, such as PDF documents, forms and emails. Optical character recognition (OCR) technologies, along with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, allow RPA to read, interpret and extract data from documents, automating processes such as form validation, order processing and accounts payable control.
This ability to automate documents increases efficiency and minimizes human error when handling information. However, document automation requires more robust analysis and training of robots, as unstructured data is more complex and variable than structured data.
Methodologies and Best Practices for RPA Implementation
- Initial Assessment and Planning: Before starting an RPA project, it is essential to carry out a feasibility analysis to understand which processes are suitable for automation. During this phase, the expected impact and cost of implementation are assessed.
- Agile development: Many organizations use agile methodologies in RPA development, implementing sprints to create and test robots quickly. Agile development allows for continuous adjustments, ensuring that robots are aligned with business needs.
- Performance Monitoring and Analysis: After implementation, it is crucial to monitor the robots to ensure that they are working as expected and delivering the projected benefits. Performance indicators (KPIs) should be established to measure impact and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Employee Training and Involvement: The adoption of RPA is most effective when employees are trained to work with the robots and understand the role of automation in the context of the company. It is important that everyone understands that automation does not replace human labor, but complements it, freeing up teams for higher value activities.
